As we learn more and more about sustainability and our impact on the environment, there is an increased focus on building homes that are the less harmful to our planet. In the building industry they determine how “green” a building is by measuring its carbon footprint. It’s important when measuring carbon footprint to take into consideration the entire lifecycle of a home not just how it operates after it’s built. This article will help explain why building log and timber homes are greener, more sustainable and have a smaller carbon footprint compared to steel .
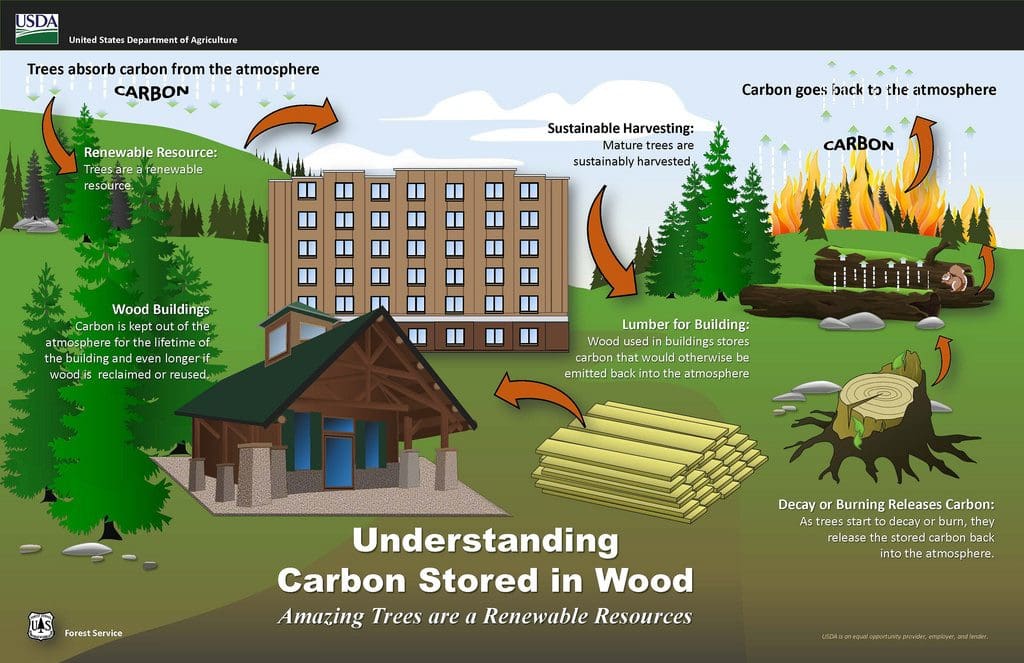
Forests and wood products are powerful tools to help mitigate the impacts of climate change. Source USDA Blog
What is a carbon footprint?
A carbon footprint, the total amount of carbon dioxide and other carbon compounds emitted directly or indirectly. For example, when you drive a car the engine burns fuel and creates a certain amount of CO2. Each vehicle can give off a different amount of CO2 depending on the fuel consumption of the vehicle. To understand the vehicle’s total carbon footprint you need to look at how it was made, what materials it’s made of, how it was transported, the CO2 it emits while you drive it, how long it will last and what will happen after it’s operational.
Trees Absorb Carbon
As trees grow they clean the air we breathe by absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere and releasing oxygen. One tree can absorb up to 48 pounds of CO2 per year for a total of 1 ton by the time it reaches 40 years old. When a tree is cut down the carbon will remain stored in the tree. Only when the tree is burnt or when it starts to decay does that stored carbon start to be released back into our atmosphere. By dry weight, wood contains approximately 50% carbon, so wood used in a building provides physical storage of carbon that would otherwise go back into the atmosphere during the decaying process, thus reducing its carbon footprint.
The Carbon Footprint of a log home
Unfortunately, of the many environmental impact studies out there, only a few of them look at the entire lifecycle of a timber or log home and the way in which it results in a much smaller carbon footprint than steel and cement homes. Steel production alone accounts for around 25% of the world’s CO2 emissions.
“In a wood building, the carbon is kept out of the atmosphere for the lifetime of the structure—or longer if the wood is reclaimed and reused or manufactured into other products. Wood stores more carbon than is emitted during its harvest, production, transport, and installation—even when transported over great distances.”
Utilization of Harvested Wood by the North American Forest Products Industry, Dovetail Partners Inc., 2012
Wood is the only major building material that is renewable and sustainable over the long term, while also being superior to steel and cement in nearly every environmental impact category. As such, log and timber homes are one of the most sustainable forms of construction, lasting substantially longer than conventional homes, and using almost 4 times less fossil fuels in manufacturing than a conventionally framed home. They are among the most energy efficient homes built today.
In addition to the wood itself, there are number of other ways that building a log or timber home reduces its carbon footprint:
1. Smaller Footings
Because wood is a naturally lighter building material, log and timber frame homes don’t require as deep and extensive concrete footings as conventional brick homes, which can save up to 11.5 tonnes in CO2 emissions.
2. Less Reinforcing Steel
Smaller footings also mean less concrete, and therefore a lower use of reinforcing steel. This reduces both the foundation costs and the carbon footprint.
3. Low Thermal Conductivity
Timber has a much lower thermal conductivity than brick, which means that there is much less transfer of outside temperatures into your home, providing more efficient temperature regulation.
4. Energy Efficient Insulation
Log and timber frame walls can be easily insulated with energy efficient materials, reducing heating and cooling costs throughout the year.
5. Reduced Embodied Energy
The overall production and transportation of timber to your home’s location takes much less energy than producing and transporting brick and other conventional construction materials.
If minimizing your carbon footprint is a priority for you when building your home, a timber or log home may be a great option for you. Check out our Log Home Galleries and Log Home Plans to give you some different ideas and concepts, and feel free to contact us if you have any further questions.



